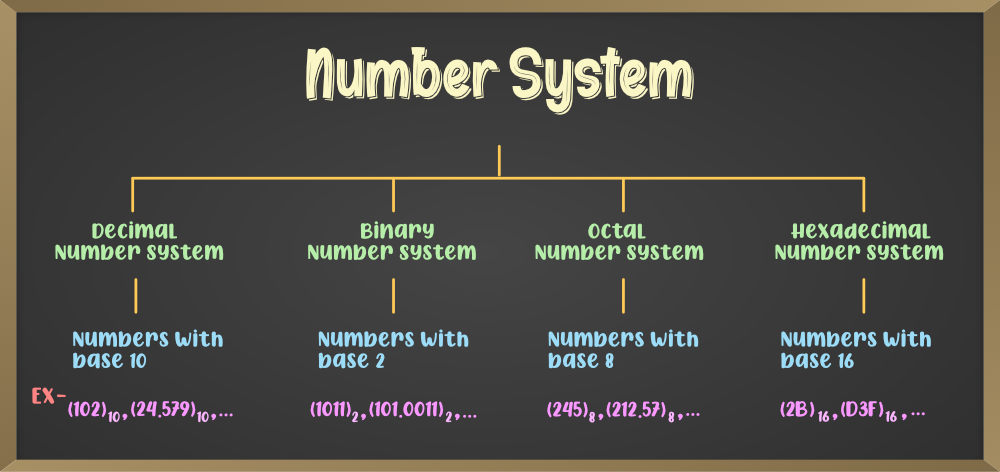
Introduction
Number systems are fundamental to mathematics and computing, providing a way to represent and work with quantities and values. They form the basis for various calculations and are used extensively in different fields, including computer science, engineering, and everyday life. In this blog, we will delve into the fascinating world of number systems, exploring their types, conversions, and applications.
Decimal Number System
The decimal number system, also known as the base-10 system, is the one we use most commonly. It consists of ten digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. Each digit's position in a number indicates its place value, with the rightmost digit representing ones, the next digit representing tens, then hundreds, and so on. For example, the number 456 in the decimal system is read as four hundred fifty-six. 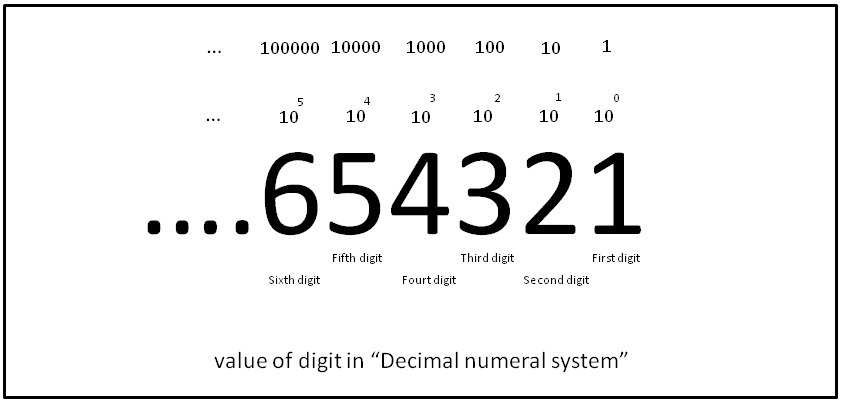
Binary Number System
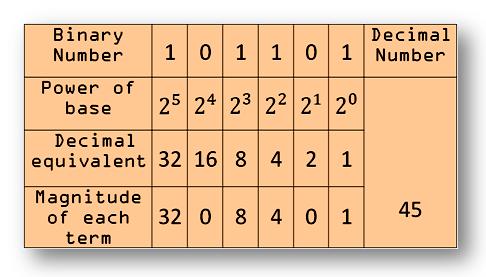
The binary number system, or base-2 system, is crucial in computer science and digital electronics. It uses only two digits: 0 and 1. Each digit's position represents a power of 2, with the rightmost digit representing 2^0 (1), the next representing 2^1 (2), then 2^2 (4), and so on. Computers use binary to represent and process data, where each 0 or 1 is a bit. For example, the binary number 1010 represents 10 in decimal.
Hexadecimal Number System
The hexadecimal number system, or base-16 system, is widely used in programming and computer memory addressing. It uses sixteen digits: 0-9 and A-F, where A represents 10, B represents 11, and so on up to F, which represents 15. Hexadecimal simplifies binary representation, as each hexadecimal digit corresponds to four binary digits. For instance, the decimal number 255 is represented as FF in hexadecimal.

Octal Number System
The octal number system, or base-8 system, is less common but still has its uses, especially in digital systems. It uses eight digits: 0 to 7. Similar to hexadecimal, each octal digit corresponds to three binary digits. The octal number 34 represents the decimal value 3*8 + 4 = 28. 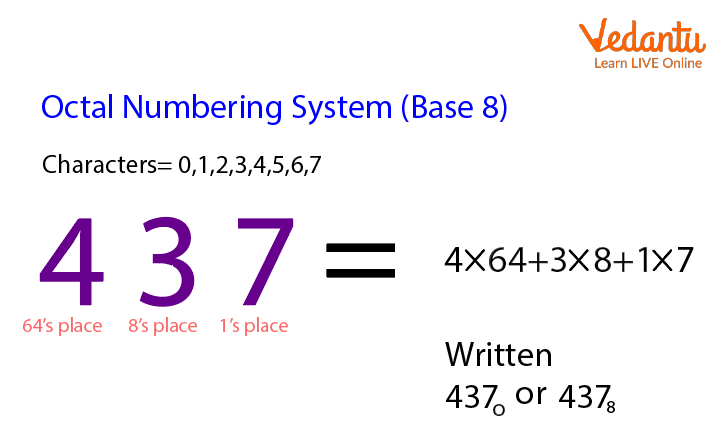
Converting Between Number Systems
Converting numbers between different bases is essential in various applications. Here's a brief overview of the conversion process:
Decimal to Binary: Divide the decimal number by 2 successively, noting the remainders, until the quotient becomes zero. The remainders, read in reverse order, give the binary equivalent.
Binary to Decimal: Multiply each binary digit by 2 raised to its position's power and add all the results to obtain the decimal equivalent.
Decimal to Hexadecimal: Divide the decimal number by 16 successively, noting the remainders, until the quotient becomes zero. The remainders, read in reverse order, give the hexadecimal equivalent.
Hexadecimal to Decimal: Multiply each hexadecimal digit by 16 raised to its position's power and add all the results to obtain the decimal equivalent.
Binary to Hexadecimal and vice versa: Convert the binary number to decimal first and then the decimal to hexadecimal.
Applications of Number Systems
Number systems find extensive applications in various fields:
Computer Programming
In programming, binary and hexadecimal are commonly used to represent and manipulate data. They simplify working with binary values and allow concise representation of large numbers.
Digital Logic
Digital circuits use binary digits (0 and 1) to process and store information. Binary logic forms the foundation of digital electronics.
Network Addressing
In computer networking, IP addresses are represented in binary or hexadecimal form for efficient routing and addressing.
Cryptography
Cryptographic algorithms and encryption schemes often use binary operations as a fundamental component in securing data.
Conclusion
Number systems serve as the backbone of mathematics and computing, providing versatile means to represent quantities and values. Understanding their conversions and applications is crucial for anyone working with computers, programming, or digital systems. Whether it's the everyday decimal system or the intricate binary and hexadecimal systems in computers, number systems are fundamental to our technological advancements.